Yamashiro forest hydrology research site (YMS)

Overview of this site
Yamashiro forest hydrology research site is located in the southern part of Kyoto prefecture. The site is in a broadleaf forest which is built up on weathered granite and the forest is also one of headstreams of Kizu River. The region used to be cleared off as it was managed as a suburban forest, until a century ago, when the green development operated by Johannis de Rijke has brought vegetation restoration. After the invasion by pine wilt disease in 1980’s, Konara oak has taken over and the forest is now regenerated. Such secondary forests are widely distributed throughout Kyoto-Osaka-Kobe and Seto Inland Sea coast area. Yamashiro research site was established to study internal mechanism of carbon circulation and to develop the flux observation method in such ecosystem. This site can be characterized by twin towers (one on the ridge and the other in the valley) to observe space variation in complex terrain. Several cooperative projects are carried out with neighboring universities to quantify the amount of fixed carbon and to find out the mechanism of carbon cycle. Our research activity covers wide range of areas which include long term continuous observation of seasonal change using automated chambers and REA observation of trace gas flux as well as common ecological investigations. Some studies are focusing particularly on high respiration activity of root and litter, and some are concentrating on the loss of noctornal flux by drainage flow or horizontal advection.
Location
| Position | 34 deg 47.687 min N (34.7948 deg N), 135 deg 50.770 min E (135.8462 deg E) |
|---|---|
| Elevation | 180-255m |
| Slope | 0~35° |
Climate
| Climate Classification | Temperate (Cfa, Temperate - Fully humid - Hot summer) | |
|---|---|---|
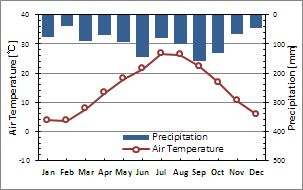
| Annual Mean Temperature | 14.7°C | (year 2000-2002) |
| Annual Mean Precipitation | 1095mm | (year 2000-2002) |
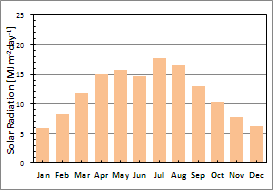
| Annual Mean Solar Raadiation | 11.9MJm-2day-1 | (year 2000-2002) |
(year 2000-2002) |
|
Ecosystem
| Vegetation | Warm temperate broadleaf forest |
|---|---|
| Area | Forest community: > 10km2 Ecosystem research area: 1.7ha, Hydrological catchment area: 1.6ha |
| Fetch | > 2km |
| Dominant Species | Quercus serrata (Konara oak), Ilex pedunculosa (japanese holly), Lyonia elliptica (tree Lyonia), Alnus Sieboldiana (alder), Clethra barbinervis (japanese sweetspire), Eurya japonica (japanese eurya), Pinus densiflora (japanese red pine), Robinia Pseudo-acacia (locust tree) |
| Canopy Height | 6m-20m, approx. 12m in average |
| Breast High Diameter | 7.4cm in average, 50.2cm in Max. (Hinoki cypress) |
| Age | Identified to be oldest red pine: 119years (BHD 34.8cm, investigated in 2000) |
| Leaf Area Index | 4.42 in summer and 2.70 in winter (LAI-2000) |
| Community Structure | Overstory, middlestory, understory |
| Soil Type | Immature soil, lm |
| More than 2km apart from major roads and inhabitable area |
Observation Period
| Period | 1 November 1999 to present |
|---|---|
| Frequency | Continuous |
Facility
| Tower Height | Ridge tower: 26.5m Valley tower: 35m |
|---|---|
| Access to Tower Top | Possible |
| Electric Power Supply | Commercial power supply AC100V 60A |
| Communication Equipment | Not available (Accessible by mobile phone) |
| Accommodation | Not available (2km to a public camp site) |
Micrometeorology
Instruments
| Name and Model | Level Upper: ridge tower Lower: valley tower | |
| Downward Short-wave Radiation | EKO MR-22 Kipp&Zonen, CM-7B | 26.2 m 36.1 m |
|---|---|---|
| Upward Short-wave Radiation | EKO MR-22 Kipp&Zonen, CM-7B | 26.2 m 36.1 m |
| Downward Long-wave Radiation | Eppley, PIR | 26.2 m - |
| Upward Long-wave Radiation | Eppley, PIR | 26.0 m - |
| Net Radiation | EKO, CN-11 | 26.2 m 36.1 m |
| Downward PPFD | LI-COR, LI190-SA | 26.2 m - |
| Upward PPFD | EKO ML-020 | -26.2 m |
| Downward PPFD below Canopy | N/A | - |
| Downward Short-wave Radiation below Canopy | EKO, MS-42 | 0.5 m - |
| All-wave Net Radiation | N/A | - |
| Air temperature | Platinum resistance thermometer Vaisala HMP-45D | 25.7, 14.2, 6.9, 5.3, 3.1 m 36.0, 20.0 m |
| Air temperature (dry-bulb) | Ventilated thermocouple wet-and dry-bulb thermometer Prede PFH-01 | 25.7, 20.0, 14.2, 8.9, 6.9, 5.3, 3.1, 1.0 m 36.0, 30.1, 25.6, 20.0, 16.0, 11.2, 6.0, 1.0 m |
| Humidity | Capacitive hygrometer Vaisala HMP-45D | 25.7, 14.2,6.9,5.3,3.1m 36.0,20.0m |
| Humidity (wet-bulb) | Ventilated thermocouple wet-and dry-bulb thermometer Prede PFH-01 | 25.7, 20.0, 14.2, 8.9, 6.9, 5.3, 3.1, 1.0 m 36.0, 30.1, 25.6, 20.0, 16.0, 11.2, 6.0, 1.0 m |
| Wind Speed | SAT (Young, MODEL85000) | 25.7 - |
| MAKINO AG-750 | 25.7, 20.0, 14.2, 8.9, 6.9, 5.3, 3.1, 1.0 m 36.0, 30.1, 25.6, 20.0, 16.0, 11.2, 6.0, 1.0 m | |
| Wind Direction | Vector instruments W200P | 26.2m 36.1m |
| Barometric Pressure | N/A | - |
| Soil Temperature | Thermocouple thermometer | 0.05, 0.12, 0.19, 0.26 m deep - |
| Soil Heat Flux | EKO, MF-81 | 0.02 m deep - |
| Soil Water Content | TDR soil-moisture meter; HYDRA HYD-10 | 0.05, 0.12, 0.19,0.26 m deep - |
| Snow Depth | N/A | - |
| Groundwater Level | N/A | - |
| Rainfall Duration | N/A | - |
| Precipitation | Tippingbucket rain gauge; 0.5mm/pulse | 10m, immediately above canopy surface, top of ecological observation tower |
Data Logger
| Sampling Period | 10sec |
|---|---|
| Averaging Period | 5min |
| Recorder | Eto electric, CADAC-2 and PC |
| Media | HDD |
| Format | Binary |
Turbulence Fluctuation Method (Eddy Covariance Method)
| System | Ridge tower: closed-path Valley tower: open-path | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Instruments
| Three-dimensional sonic anemometer-thermometer | KAIJO DAT-600-3T (Ridge & valley tower) |
Sensor span | 0.2m |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level | 25.7, 36.1 m | ||
| Height from Canopy Surface | > 10 m | ||
| Gas Analyzer (Closed-path) | LI-COR LI-6262 (ridge tower) | Distance between gas intake and analyzer | approx. 30m |
| Height of intake | 25.7 m | ||
| Height from Canopy Surface | > 10 m | ||
| Distance between gas intake and analyzer | 0.3 m | ||
| Gas Analyzer (Open-path) | LI-COR LI-7500 (valley tower) | Level | 36.1 m |
| Height from Canopy Surface | > 10 m | ||
| Distance between gas intake and analyzer | 0.3 m |
Data Logger
| Sampling Method | Continuous |
|---|---|
| Averaging Period | 0 sec |
| Sampling Frequency | 5Hz |
| Filters for Antialiasing | Available |
| CutOff Frequency | 24 Hz |
| Recording Range | All data |
| Recorder | TEAC DR-M3 |
| Media | MO |
Flux Calculation
| Calculation Period | 1800s | |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Detrending | w, u, Ta, CO2, H2O |
| Coordinate rotation | Corrected | |
| Line Averaging | Not-corrected | |
| Sensor Separation | Not-corrected | |
| Humidity Correction of Virtual Temperature | Not-corrected | |
Vertical profiling CO2 Concentration in Canopy
| Instruments | LI-COR LI-6262 |
|---|---|
| Concentration of Calibration Gas | 0, 400ppm |
| Sampling | 10 sec |
| Sampling Period | Every 120 seconds at a level x 8 levels |
| Averaging Period | 10 sec |
| Recorder | PC |
| Media | HDD |
| Format | Text |
| Purpose | To obtain the vertical profile of CO2 concentration inside and above canopy |
Relaxed Eddy Accumulation (REA) Method
| item | Trace gas flux | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Water Balance
| Precipitation | Tippingbucket rain gauge (IKEDA RT-5) 10m in height | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Outlet Flow | Float type water-level gauge (IKEDA ATR-105) installed on the weir built in valley (catchment area 1.6ha) | ||
Other Observation
Photosynthesis
| Method | Photosynthesis of sunny crown, transpiration rate, diurnal variation of stomatal conductance |
|---|---|
| Instrument | LI-COR LI-6400 |
| Observation Frequency | Several times a year, on the basis of typical air temperature and vapor pressure deficit |
Soil Respiration
| Method | Automatic closed chamber method |
|---|---|
| Observation Frequency | Continuous |
Litter
| Method | Litter trap |
|---|---|
| Observation Frequency | Once a month in defoliation period |
Biomass
| Method | Diameter, height |
|---|---|
| Observation Frequency | Every 5 years |
Sap Flow
| Method | Heat Pulse Method |
|---|---|
| Observation Frequency | Continuous |
Reference
KOMINAMI Yuji, JOMURA Mayuko, ATAKA Mioko, TAMAI Koji, MIYAMA Takafumi(2012): Heterotrophic respiration causes seasonal hysteresis in soil respiration in a warm-temperate forest. Journal of Forest Research, 17(3):296-304.
JOMURA Mayuko, KOMINAMI Yuji, ATAKA Mioko(2012): Differences between coarse woody debris and leaf litter in the response of heterotrophic respiration to rainfall events. Journal of Forest Research, 17(3):305-311.
MAKITA Naoki, HIRANO Yasuhiro, DANNOURA Masako, KOMINAMI Yuji, MIZOGUCHI Takeo, ISHII Hiroaki, KANAZAWA Yoichi (2009): Fine root morphological traits determine variation in root respiration of Quercus serrata. Tree Physiology, 29(4):579-585
KOMINAMI Yuji, JOMURA Mayuko, DANNOURA Masako, GOTO Yoshiaki, TAMAI Koji, MIYAMA Takafumi, KANAZAWA Yoichi, KANEKO Shinji, OKUMURA Motonori, MISAWA Noriko, HAMADA Shogo, SASAKI Taizo, KIMURA Hitoshi, OHTANI Yoshikazu (2008): Biometric and eddy-covariance-based estimates of carbon balance for a warm-temperate mixed forest in Japan. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 148(5):723-737
KOMINAMI Yuji, MIYAMA Takafumi, TAMAI Koji, NOBUHIRO Tatsuhiko, GOTO Yoshiaki (2003): Characteristics of CO2 flux over a forest on complex topography. Tellus B, 55(3):313-321
DANNNOURA Masako, KOMINAMI Yuji, OGUMA Hiroyuki, KANAZAWA Yoichi (2008): The development of an optical scanner method for observation of plant root dynamics. Plant Root, 2:14-18
JOMURA Mayuko, KOMINAMI Yuji, DANNOURA Masako and KANAZAWA Yoichi (2008): Spatial variation in respiration from coarse woody debris in a temperate secondary broad-leaved forest in Japan. Forest Ecology and Management, 255(1):149-155
TAMAI Koji, KOMINAMI Yuji, MIYAMA Takafumi, GOTO Yoshiaki, OHTANI Yoshikazu (2008): Topographical Effects on Soil Respiration in a Decious Forest -The Case of Weathered Granite Region in Southern Kyoto Prefecture-. Journal of Agricultural Meteorology, 64(4):215-222
MIYAMA Takafumi, KOMINAMI Yuji, TAMAI Koji, GOTO Yoshiaki, Teruhiko Kawahara, JOMURA Mayuko, DANNOURA Masako (2006): Components and seasonal variation of nighttime total ecosystem respiration in a Japanese broadleaved secondary forest. Tellus B, 58(5):550-559
GOTO Yoshiaki, KOMINAMI Yuji, MIYAMA Takafumi,TAMAI Koji, KANAZAWA Yoichi (2003): Aboveground Biomass and Net Primary Production of a Broad-leaved Secondary Forest in the Southern Part of Kyoto Prefecture, Central Japan. Bulletin of the Forestry and Forest Products Research Institute, 2(2):115-147 [in Japanese with an English abstract]
Research Fund
- Major Facility Installation for Carbon Dioxide Monitoring, Forestry Agency, MAFF*
- Research Grant, FFPRI
- Research Fund (Evaluation, Adaptation and Mitigation of Global Warming in Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries: Research and Development), MAFF*
- Grant in Aid of Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology, MEXT**
- Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research, MEXT**
- Global Environment Research Account for National Institutes, MOE***
* MAFF: Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan
** MEXT: Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
*** MOE: Ministry of the Environment
Researchers
Yuji KOMINAMI, Takafumi MIYAMA, Koji TAMAI
Cooperative Researchers
Susumu TOHNO, Motonori OKUMURA, Masako DANNNOURA, Mioko ATAKA (Kyoto Univ.), Naoki MAKITA, Akira MATSUMOTO, Kenichi YOSHIMURA (Kobe Univ.), Mayuko JOMURA (Nihon University)
Contact Information
Forest Environment Group, Kansai Research Center,
Forestry and Forest Products Research Institute (FFPRI)
Address: 68 Nagaikyutaroh, Momoyama, Fushimi, Kyoto, 612-0855 JAPAN
TEL: +81-75-611-1201 (main)
 Top of Page
Top of Page